A vacuum flask reduces heat loss to preserve hot drinks
In general, the human blood temperature is at around 37 degree Celsius and we always keep it stable, just to survive. The task for a vacuum flask is also to keep a stable temperature for the liquid it stores inside, and in order to do that, it has a special design to help reduce the heat loss. It is very simple and effective, but how does a vacuum flask reduce heat loss?
Heat traveling mechanism
Before we can understand how a vacuum flask reduces the heat loss, we need to understand a basic thing: how heat travels around the world.
A vacuum flask can reduce the heat loss for several hours.
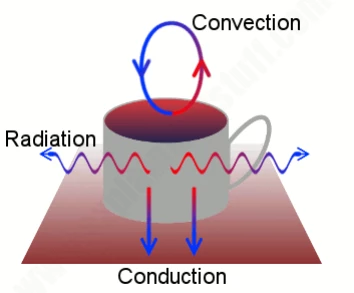
Heat is general energy in three different ways called conduction, convection, and radiation. It moves through the air, liquid, and solid things.
If we touch something cold, the heat moves from our body straight to the object given a direct connection in place between our hand and the cold object. The heat conduction occurs only when things are connected directly.
Convection can happen anytime and anywhere without a direct connection. Boiling water is a way of using heat convection. The hot air is lighter than the cold air so that it always rises. On the other hand, the cold air always goes downwards. For example, when we turn on the air conditioner, its fan blows the hot air out and it will rise. People thus feel cooler from the floor.
Radiation is slightly different from conduction and convection. When a thing is hot, it radiates light. That is why fires or metal is heated, it always gives off light. This happens because the atoms in hot objects become "excited" and unstable, and they start moving around as fast as the heat increases, gaining extra heat energy from the fire. Since the atoms are unstable, they move very fast and return quickly to their normal state and transfer the energy they have into the light.
Why a hot drink goes cold
A hot drink cools through a mixture of conduction, convection, and radiation
Suppose there is a hot teapot. It needs to be drunk quickly before it gets cold. But why is it cooling? Boiling water has a temperature of 100 degree Celsius, while room temperature is more likely to be 15-20 degree Celsius, depending on the weather and whether we have an air conditioner working. Since the water in our tea is much hotter than the room, heat flows rapidly from the teapot to the surrounding air.
Some heat will be lost by conduction: because the teapot stands on a table, heat will flow directly downward and disappear that way. The air right above and around the pot will be warmed by the heat and starts moving around, so more heat will be lost by convection, and also there will be some heat lost by radiation.
Altogether, conduction, convection, and radiation will turn the hot tea into something cold. If we want the tea to stay hot, we need to stop the conduction, convection and radiation from happening. We can do that by pouring the tea into a vacuum flask. But how does a vacuum flask reduce the heat loss
How does a vacuum flask reduce heat loss?
In order to preserve heat for a long time, people create a vacuum layer to hold the glass jar and shell, because a vacuum is a material free medium, which means good insulation. It limits the phenomenon of heat transfer from water to the glass bottle to the shell.
People often make bottles with a small mouth, or use a mechanism to take water out without having to lift the cap, thus limiting the space for evaporation, which is to limit convection. Besides, the silver coating of the glass also helps achieve optimum heat retention.
A vacuum flask is like a super-insulated jug. Most versions have a glass refill inside and an outer plastic or metal case. It is separated by two layers of glass with a vacuum in between. The glass is a material that is usually lined with a reflective metal layer.
With the stopper removed, we can clearly see the reflective glass inside this vacuum flask.
With these few simple features, a vacuum flask prevents all heat transfer via either conduction, convection or radiation. The vacuum between two glass layers prevents conduction. The convection is prevented by the tight stopper which prevents the air from entering or leaving the flask.
How about radiation? When infrared radiation tries to leave, the reflective lining from the inner glass reflects it straight back in again. The heat has no way out of a “perfect” vacuum flask and the tea will be stored hot for several hours. The vacuum flask also works for cold drinks.
Should you have any questions, wish to share your ideas about vacuum flasks or request a quotation, please send us an email to: export@rangdong.com.vn.
Our website: vacuumflask.rangdong.com.vn